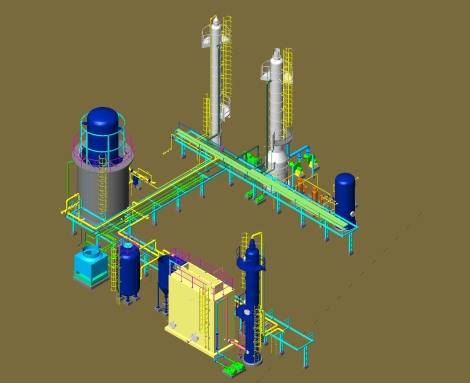
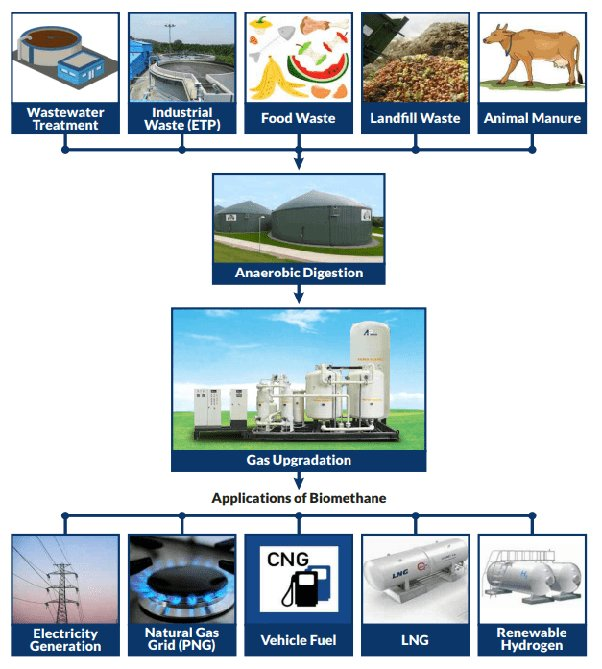
Agricultural waste, manure, municipal garbage, plant matter, sewage, green waste, and food waste sugarcane press mud can all be broken down into Biogas without oxygen (Anaerobic Process). This mixture becomes bio-compressed natural gas after additional purification and processing. It is a cleaner alternative to fuels like gasoline and diesel and is similar to natural gas in terms of composition and quality.
In India, bio-CNG has enormous potential, particularly as a substitute for the more popular CNG and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or Liquefied Petroleum Gas). Bio-CNG can be a better substitute for CNG and LPG in hotels, households, automobiles, etc.